
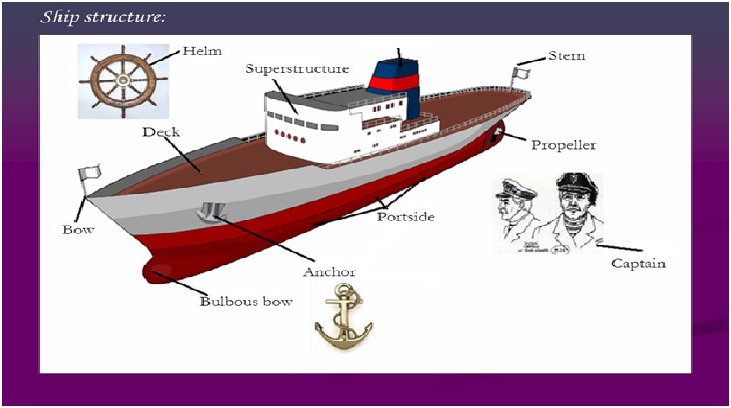
In the modern maritime universe, the ships are significant in executing specialized missions, including mining, fishing, research, and defense.
This type of water vessel moves while carrying either goods or passengers connecting continents, countries, etc. What is a Ship in Freight Terms?Ī ship is an extensive water vessel that travels the oceans, seas, and deep waterways. Those precious minerals may include diamond, copper, gold, silver, zinc, cobalt, manganese, etc. That form of activity is significant in enhancing the navigability of those specific areas.Įlsewhere, some other water vessels extract different types of minerals and valuable stones from the seabed. Specifically, dredging vessels are efficient at extracting sand and other marine deposits from the sea beds. Some vessels are significant in deep-sea mining and extraction activities in the ocean, seas, and lakes. Volatile goods (crude oils), weaponry, clothes, house merchandise, electronics, containers, automobiles are just some of the typical goods often transported via vessels. Luggage transportation amongst countries and territories has been one of the most affordable transport modes for use by importers. Luggage TransportationĪlso, vessels offer great flexibility and reliability in the transportation and delivery of goods across long distances especially cross country delivery. Moreover, engineers have greatly designed and developed modern large cruiser ships to transport passengers across various countries, borders, and cities to date. Since time immemorial, even before world war I, colonialists used to ferry slaves from the African continent to the USA via large ships. These vessels would even transport passengers across countries and even continents. Since the term “vessel” incorporates a wide variety of specific water automobiles, consequently, the vessels do have a wide range of functions as outlined below: Passenger Transportationīoats, large ships, ferries, etc., are efficient water transport modes for ferrying passengers/travelers across different water bordering places or venues.

In addition to this, a vessel includes large boats and ships regardless of whether they are passenger or luggage types. Some users also appreciate a vessel as a craft used for water transportation and usually bigger or massive than a rowboat. Therefore, according to this definition, a vessel would include all such machines, from boats to large ships. Generally, a water vessel widely refers to any watercraft that navigates the water bodies. What are the Advantages of a Stiff ship and a Tender Ship?.What is the Difference Between a Stiff Ship and a Tender Ship?.What Material is Used to Make the Bottom of a Ship?.How do You Determine a Vessel Position?.What are the Differences Between a Vessel and a Tank?.How Do you Find out Who Owns a Shipping Vessel?.At what Point Does a Boat Become a Ship?.What are the Defining Differences Between Ship, Vessel, and Boats?.What are the Different Variations of a RoRo (Roll-on/ Roll-off) Ship?.What are the Different Sizes of Container Ships?.What are the Advantages of a Bulk Carrier Vessel?.How Many types of Bulk Carriers are There?.What are the Different types of Tanker Ships?.Why is a Ship Transporting Goods Called a Vessel?.Is an Aircraft Carrier a Ship or a Boat?.What is the Difference Between Ship and Steamer?.What is the Difference Between the Mother Vessel and the Feeder Vessel?.What is the Capacity of a Mother Vessel?.What is the Difference Between Container and Vessel?.What is the Difference Between a Vessel and a Ship?.Side note here: DP1 vessels are not very common, with DP2 and DP3 becoming more common due to the additional level of safety they provide. Systems also must be physically separated for DP3. Systems may also be required to be watertight depending on the vessel and damage to one system must not affect the backup. DP3 takes DP2 one step further with the ability to continue operation with the failure of an active or static component, even with the total loss of the equipment in a compartment to fire or flood. The redundant system must provide the ability to keep station until work can be safely stopped, and the transfer of operations must be automatic. DP2 fulfills DP1 requirements but can also keep station with the failure of an active component. DP1 systems are the most basic, with the ability to keep their position in automatic mode. The levels build on each other, with each succeeding level having the abilities of the previous level. According to IMO guidelines, DP systems are rated DP1, DP2, or DP3.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
